SEO Localization Strategy (For Payroll Navigator Series)
Steps to build an effective SEO Localization Strategy For Payroll Navigator series. Step 1 : Prepare your site's URL Structure. Step 2 : Find your local search competitors - Example for Payroll Navig…
Steps to build an effective SEO Localization Strategy For Payroll Navigator series
- Step 1 : Prepare your site's URL Structure
- Step 2 : Find your local search competitors - Example for Payroll Navigator Series
- Step 3 : Identify relevant keywords
- Step 4 : Process to build your keyword map for Payroll Navigator Series
- Step 5 : Use keywords in content and scale
- Step 6 : Links to Pillar Pages or with other content
- Step 7 : Track your SEO KPI and metrics
1. Prepare your site's URL Structure
- Use the locale-specific URLs
Before localizing your content (e.g the Payroll Navigator series) to a new language, we will have to fix the website’s URL structure. We will need to use the locale-specific URLs. For example https://www.sdworx.it . This is a country specific domain and shows clear geotargeting.
Example of SD Worx locale-specific URL Structure we already have:
For Corporate website:
https://www.sdworx.com/en-en/resources/payroll-navigator-2024/should-i-outsource-payroll-or-keep-it-house
For UK website:
https://www.sdworx.co.uk/en-gb/resources/uk-payroll-navigator-2024/should-i-outsource-payroll-or-keep-it-house
- To geo-target your site on a page level.
To use 'hreflang' to inform Google which pages apply to which locations or languages.
Use hreflang to tell Google about the variations of your content, so that we can understand that these pages are localized variations of the same content.
hreflang or the HTML lang attribute to detect the language of a page; instead, we use algorithms to determine the language.(NOTE: Please let me know when you finish publishing your page on Navigator series, I will add the necessary hreflang tag.)
2. Find your local search competitor
Knowing who you’re competing against is crucial in SEO. It is even more crucial when going global. Here is how to find your local SEO competitors in a new market:
- Distinguish local SEO competitors
When trying to grow in a new country, you need to know who your local search competitors are. They may differ from your usual business or product competitors. Even if you sell the same product or service or have the same type of offer as them, your local competitors may not be doing SEO at all. - Look at who your local search competitors are:
Find out who is showing up in that specific market for the primary keywords you want to rank for. The easiest way to verify this is by checking what Google displays in local search results. If not, please use tool like the Google Location Changer. - Search like a local
Use relevant keywords. Don’t worry about having the exact localized phrase yet. (e.g make a search for 'onboarding automatisé' in french language for French website ) - Learn from the rankings
Analyze the top search results. This can reveal interesting insights into:
1. How competitors structure their content for the local language
2. The actual keywords they're targeting
3. Even interesting nuances, like using English phrases within German descriptions.
Bonus Tip :Prioritize the local language first. If results are lacking, consider a mix based on audience research. Remember:
|
Competitor research For the Payroll Navigator series
- Make a Search of your competitor e.g search for Payroll competitor in Belgium market.
- On the Google Location Changer tool (https://seranking.com/google-location-changer.html), type your keyword, choose your country, choose your language.
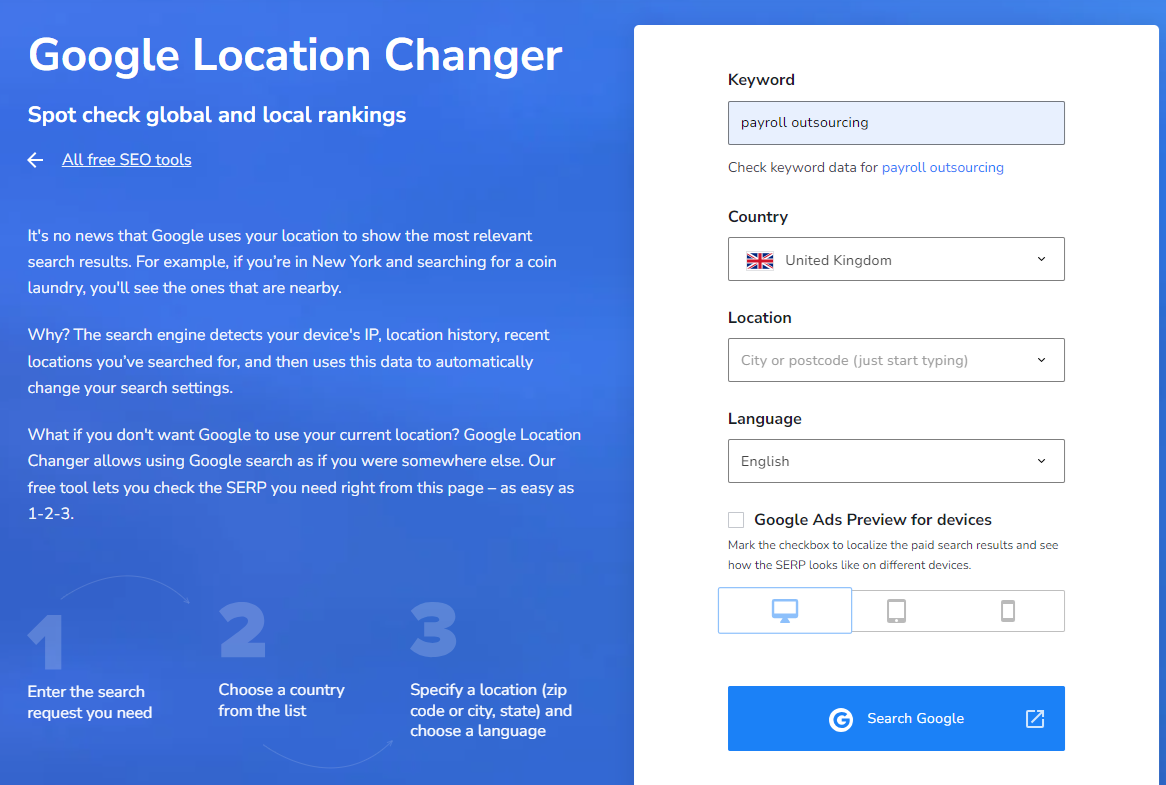
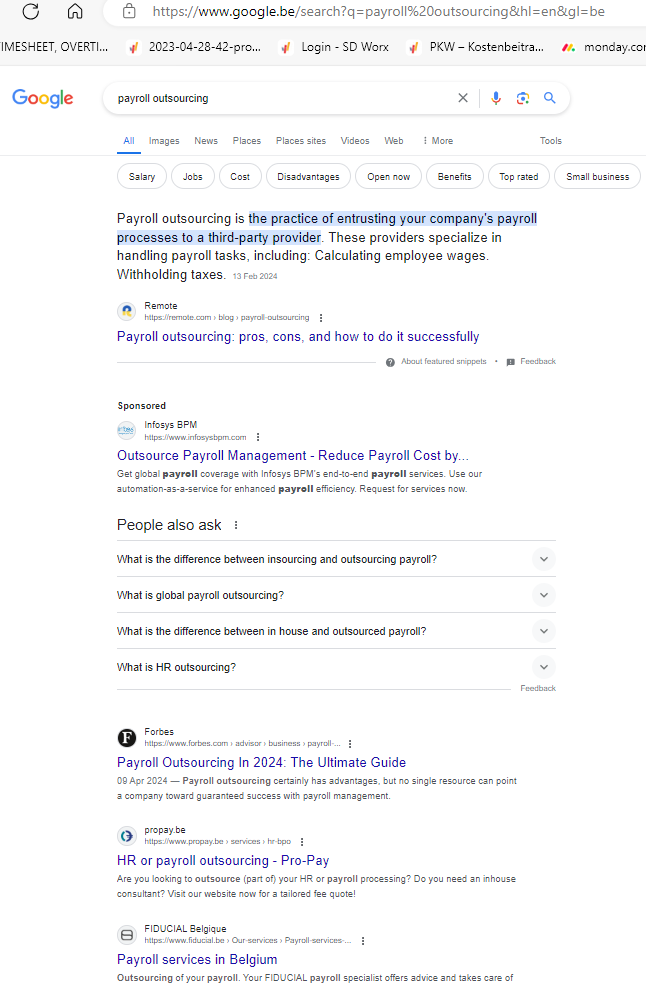
- The results will display a list of your competitors for your keywords. See Screenshot below.
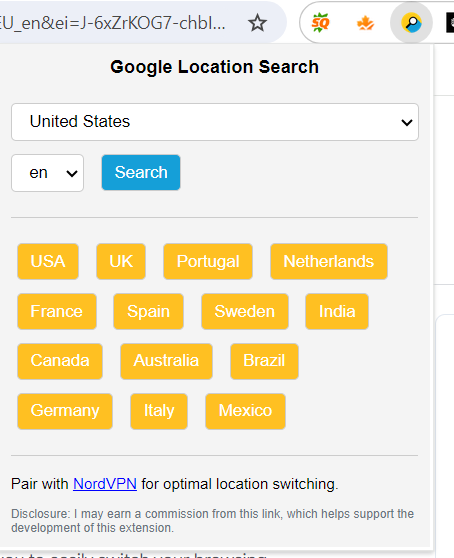
Google Search Location changer browser extension (Another Option)
Instead of using the Google Location Changer link, you can use the Google Search Location changer Chrome browser extension.
1. Search for the extension on google.com. Type 'google search location changer'
2. And download the extension.
3. Install it on your Chrome Browser. It should look like this. You will be able to choose your country and then the language.
3. Identify relevant keywords
Now that you have identified your competitors, you can start researching the keywords that lead to conversions:
- Focus on long-tail keywords
- Regardless of language, SEO thrives on long-tail keywords, which are detailed phrases with 3+ words that describe your product or service and have clear search intents.
- When localizing international content, user intent is key and it does not have to be homogeneous across markets.
- Long-tail keywords have higher conversion rates because they are typically used by users who are closer to making purchase decisions.
Recommendation: If you haven’t yet pinpointed the exact phrasing, begin with a translated version of your keywords. This is a good starting point.
Use AnswerThePublic to get the related keywords, or some keyword ideas.
- Pay attention to search volumes
This data provides insights into how people typically phrase their queries. If you notice a particular phrasing taking on the highest search volume, it is likely the most common and effective way to reference your product or service in that language.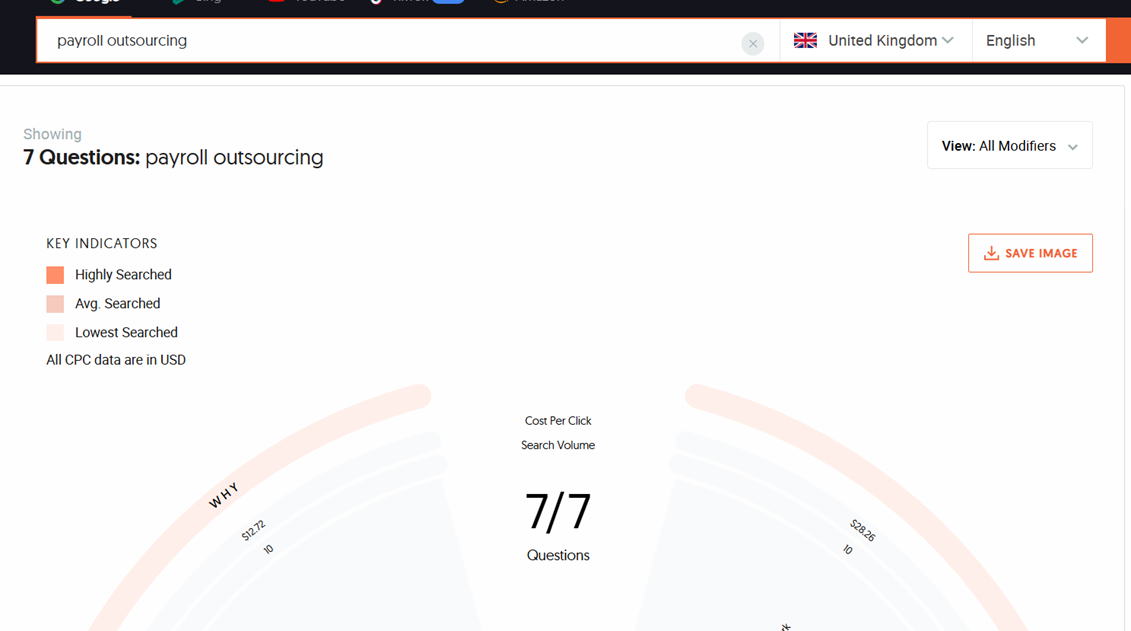
4. Process to build your keyword map for Payroll Navigator Series
Process to build your keyword map for Payroll Navigator Series
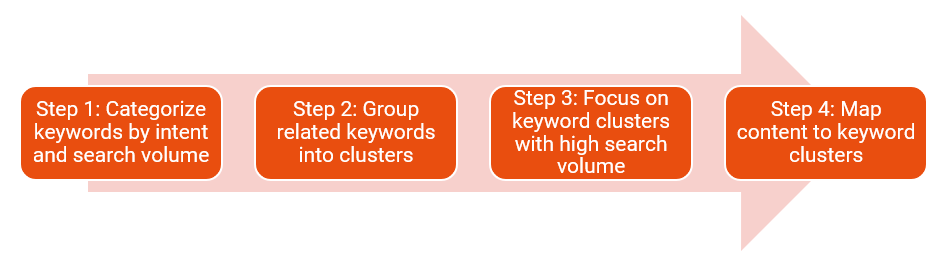
Click for more details on Keyword Clusters
Step 1 : Categorize keywords by intent and search volume
Variances in user search intent, demand, and phrasing depend on language and culture.
NOTE: Some practical experience shows that blind translation does not work
Example 1 :Informational keyword localization example:Imagine you need to localize a blog about “what is process management” from English to German to reach your audience in Germany. 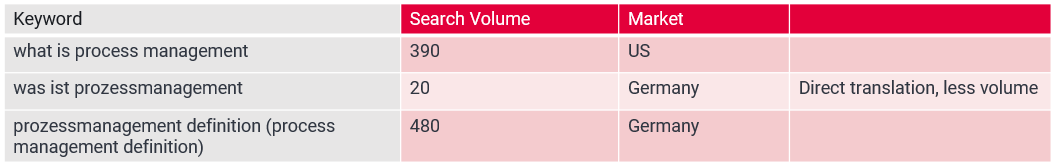
|
Recommendation: Identify keywords in the local language with matching search intent to the non-native keyword.
Example 2 :Transactional keyword localization example :Let’s say a company based in the US has a popular “heated tobacco” product. They plan to use an SEO-driven approach to expand into Hungary. 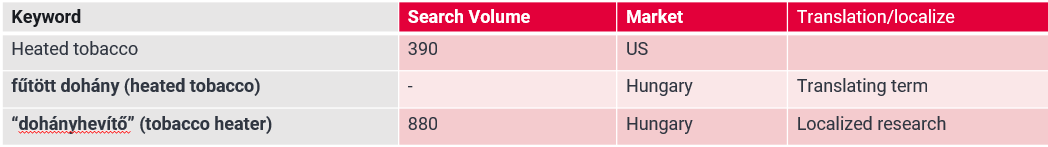
|
Recommendation : Check local keyword search volume and consider similar phrases.
Step 2 : Group keywords into clusters
Group related keywords with similar intent (informational vs. transactional) into clusters.
This helps you structure your content effectively. I have already explained about keyword cluster on my SEO and Content marketing presentation.
Step 3 : Focus on Keyword clusters with high search volume
Focus on keyword clusters with high search volume (those most likely to lead to sales or signups) and ones that closely match your existing content from your home market. These will be easier to localize and will save you time and resources.
Remember:1. Search intent and phrasing: Learn about how your target audience phrases their searches. 2. Grammar matters: Google understands synonyms and alternative phrasings, but always keep your content grammatically correct for a better user experience. |
Step 4 : Map content to keyword clusters
Build your content strategy around keyword clusters. Determine each cluster’s appropriate content type (informational, transactional, etc) based on search intent.
5. Use keywords in content and scale
Now that your keyword map and content topics are ready, you adapt the payroll navigator content for targets your chosen keywords for better reach. Here are some on-page SEO to consider when using keywords in your content and scaling your efforts:
SEO Title: Focus Keyword Here l Brand Name (no limit or can be 60 characters, may be reduced length from H1 but should be a close match) SEO Description: Focus keyword at the start and CTA at the end. (155 characters) URL: /language-subdirectory/longtail-focus-keyword [H1] Title of the content Introduction •Bullet point notes on what the content writer could write in the introduction •Use the focus keyword at the beginning. [H2] Subheading |
SEO Title and Description |
|
URL Structure |
|
Keyword Usage | Add your target keywords naturally into your content’s SEO titles, descriptions, subheadings, and body text. |
6. Links to Pillar Pages or other content
Consider how your planned topic relates to the content you have already created or other pieces you plan to create.
For Payroll Navigator series, we already have the existing Payroll resources page as a Pillar Page. So we will need to select the right pillar page well before publishing it.
https://www.sdworx.co.uk/en-gb/resources/payroll
7. Track your SEO KPI and metrics
Choose your SEO Dashboard to track the SEO performance per country for the Payroll Navigator Series.
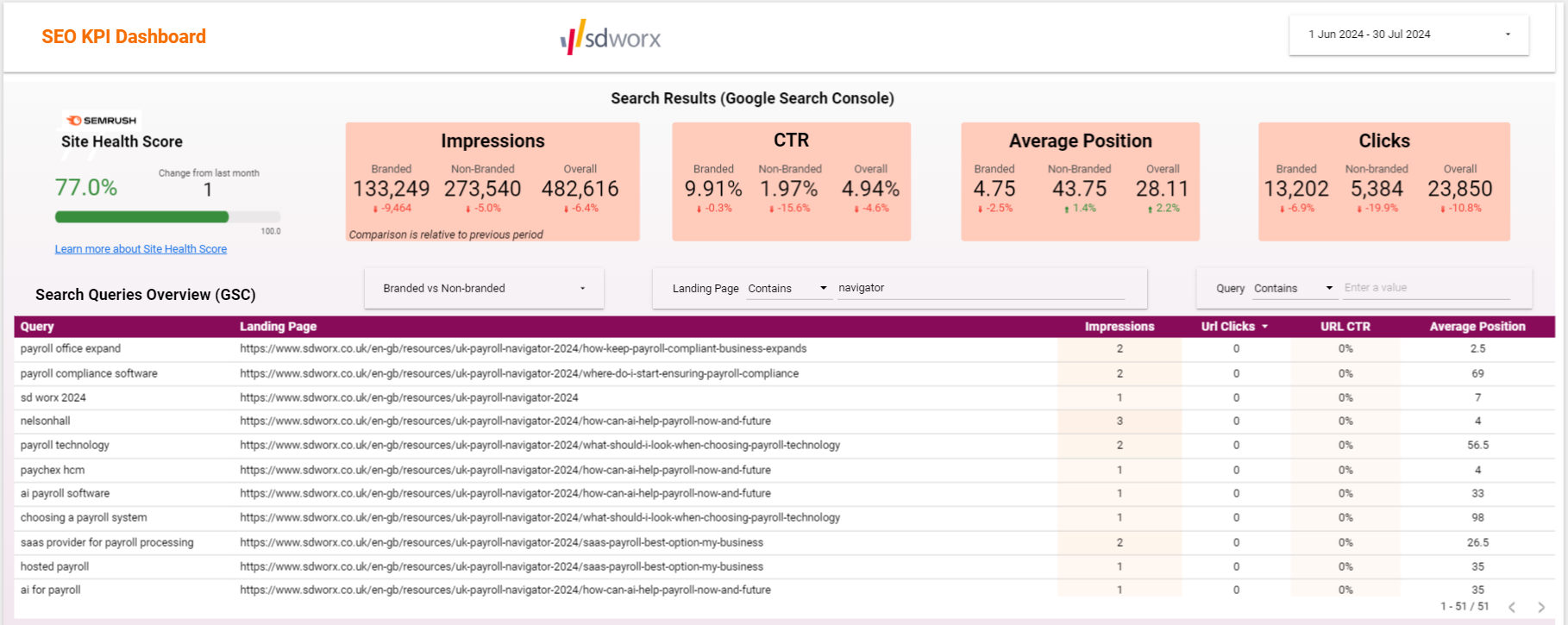
How to get the landing pages of the Payroll Navigator series?
On the landing page drop-down menu, type 'Payroll'. The list of pages will load. You can then see the Search Results (impressions, clicks, URL CTR, Average position) and can then take necessary actions to improve the results.
You can check the Organic Visibility, Organic website traffic and view your ranking of your targeted keywords.
On the above screen you can see the payroll navigator series pages for UK website have received very low impressions and no clicks at all for the period June to July 2024. This means that the Pages are NOT being seen enough by people who will find your information useful and worth reading on the Search engines and they are not compelling enough for people to click on them.
- Impressions refer to the number of times your web pages have appeared in search engine results for a specific query. Please note Impressions are important because someone needs to see a link to your website in order to click to visit it
- Clicks represent the number of times users actually clicked on your link and visited your website.
- Low clicks may result from various factors, such as poor title optimization, competition, or changes in search result layouts.
- However, high impressions alone don’t guarantee success; they need to be complemented by user engagement (clicks) to be truly effective.
Action Plan to get impressions, clicks and CTR for Payroll Navigator Series : On-page optimisation, internal links, call to action.
How did we do?
Advanced AI Prompts for SEO and Content
Best practices for Wikipedia

